mood incongruent psychotic features
/mood-incongruent-380034-color01-8eab959cdd0244ccbf94cd7e2a366f42.png) Mood Congruence and Incongruence in Bipolar Disorder
Mood Congruence and Incongruence in Bipolar DisorderCOVID-19 is an emerging and rapidly evolving situation. Account name Save an appointment to archive E-mail citation Add to Collections Add to My Bibliography Your search saved Create a file for external dating management software Your RSS Feed Full text links Actions Share Page navigation Incongruent psychotic characteristics in bipolar disorder: family aggregation and suggestive linkage to 2p11-q14 and 13q21-33 Membership Incongruent psychotic characteristics in bipolar disorder: family aggregation and suggestive linkage to 2p11-q14 and 13q21-33 Authors Membership Summary Objective: Incongruent psychotic characteristics of bipolar disease can mean a more severe form of the disease and can represent phenotypic manifestations of susceptibility genes shared with schizophrenia. This study seeks to characterize clinical correlates, family aggregation and genetic linkages in subjects with these characteristics. Method: The topics of the National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH) Genetics Initiative Bipolar Disorder Collaborative cohort, which consists of 708 families recruited in 10 academic medical centers. Subjects with psychotic characteristics consistent with mood and mood were compared in clinical variables. The family aggregation was tested using a predictive model of widespread bands and estimation equations. A link analysis was performed throughout the genome that incorporates a covariate of incongruity of humor. Results: The psychotic characteristics incongruent with the moods were associated with a higher rate of hospitalization and attempted suicide. A taste with incongruity of humor predicted the incongruity of relatives with bipolar disorder I compared to all other subjects and compared to subjects with congruent psychosis of humor. The presence of psychotic characteristics incongruent with the mood increased the evidence to link the chromosomes 13q21-33 and 2p11-q14. These logarithms of probabilities ratio scores (ODL) and their increase in the base met empirical criteria of genome worldwide suggestive for significance. Conclusions: The psychotic characteristics incongruent with the mood showed evidence of a more severe course, family aggregation and suggestive link to two chromosomal regions previously involved in the susceptibility of main mental illness. Finding 13q21-33 supports previous evidence of bipolar disorder/skezophrenia overlap in this region, while finding 2p11-q14 is, to the authors' knowledge, the first to suggest that this region of link schizophrenia could also host a gene of susceptibility of bipolar disorder. Comment in Similar articles Cited by 32 articles Types of publication MeSH Terms Related information Grant support Link Out - more resources Total Text sourcesMedicalResearch MaterialsMiscellaneousNCBI Literacy resources National Library of Medicine

Psychotic disorders Med ppt download

PPT - Differential Diagnosis PowerPoint Presentation, free download - ID:2100871
PDF) Mood-Incongruent Psychotic Features in Bipolar Disorder: Familial Aggregation and Suggestive Linkage to 2p11-q14 and 13q21-33

CHAPTER FIVE Mood Disorders. Basic definitions Unipolar mood disorders Special topic: Depression & interpersonal relationships Bipolar mood disorders. - ppt download

Mood-Incongruent Psychotic Features in Bipolar Disorder: Familial Aggregation and Suggestive Linkage to 2p11-q14 and 13q21-33 | American Journal of Psychiatry

Bipolar disorder: discussion points

Pharmacological Management of Bipolar Disorder
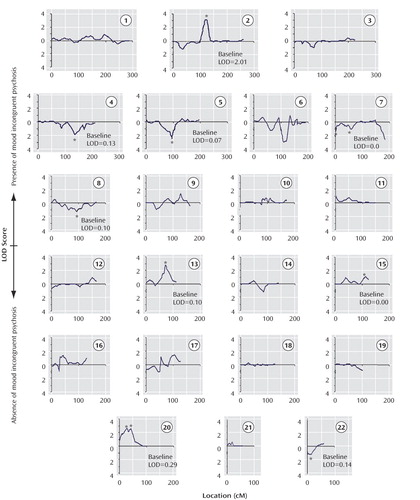
Mood-Incongruent Psychotic Features in Bipolar Disorder: Familial Aggregation and Suggestive Linkage to 2p11-q14 and 13q21-33 | American Journal of Psychiatry

Melancholic and Psychotic Depression - Diagnosis and Management

PPT - Differential Diagnosis PowerPoint Presentation, free download - ID:2100871
Mood disorders PSYCHIATRY REVISION NOTES

New tricks of an Old Antidepressant - ppt download

Clinical Impression. Bipolar I Disorder Also known as Bipolar Affective Disorder A psychiatric diagnosis that describes a category of mood disorders. - ppt download

Mood Disorders - online presentation
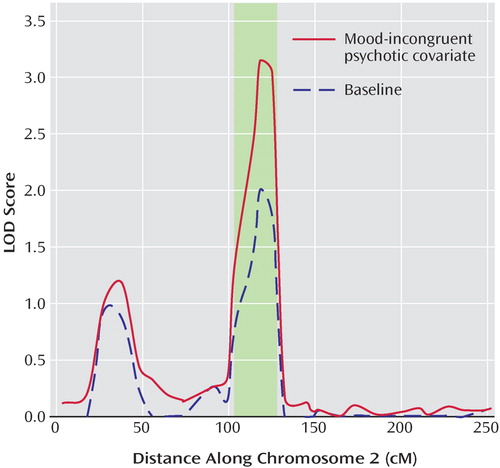
Mood-Incongruent Psychotic Features in Bipolar Disorder: Familial Aggregation and Suggestive Linkage to 2p11-q14 and 13q21-33 | American Journal of Psychiatry
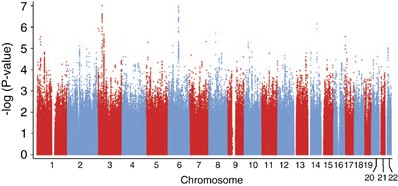
Genome-wide association of mood-incongruent psychotic bipolar disorder | Translational Psychiatry

PDF) Mood-Incongruent Psychotic Features in Bipolar Disorder: Familial Aggregation and Suggestive Linkage to 2p11-q14 and 13q21-33

Other psychotic disorders Dr C Kotzé. Classification Schizophrenia Schizophreniform disorder (1 – 6 months) Brief psychotic disorder (1 day – 1 month) - ppt download

Psychosis in Bipolar Disorder: Symptoms & Strategies to Cope
DSM-5 and mood disorders: The Good, the Bad and the Ugly - PDF Free Download

What Is Psychotic Depression?

Bipolar I Disorder with Psychotic Features | Symptom Media
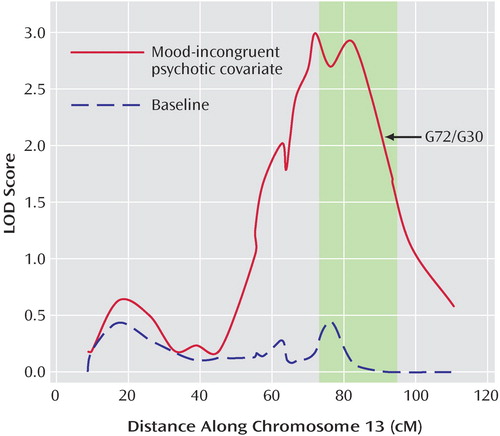
Mood-Incongruent Psychotic Features in Bipolar Disorder: Familial Aggregation and Suggestive Linkage to 2p11-q14 and 13q21-33 | American Journal of Psychiatry
V. Mood Disorders It was called as a "depressive disorders" or as an "affective disorders" or as "depressive neuroses". In DSM-III-R, changed as "Mood. - ppt download
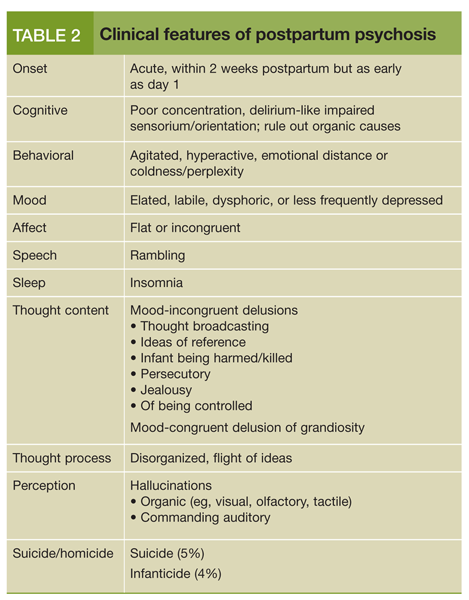
Postpartum Psychosis: Updates and Clinical Issues

Major Depression with Psychotic Features – BrightQuest Treatment Centers
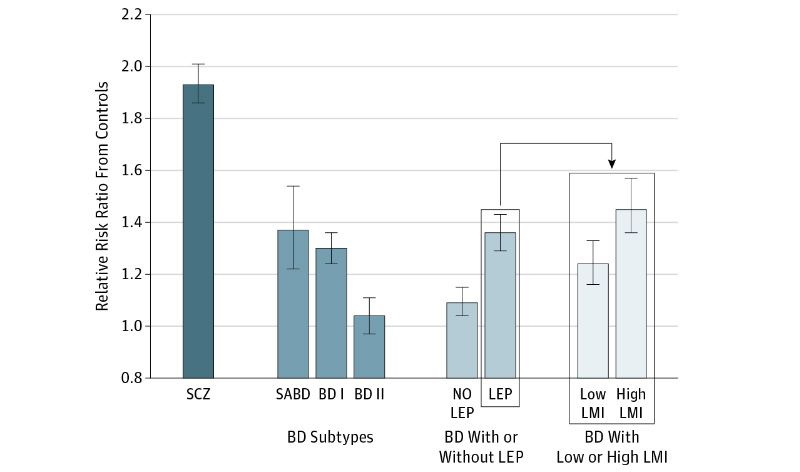
Mood-incongruent bipolar disorder tied to polygenic liability of schizophrenia | MDLinx
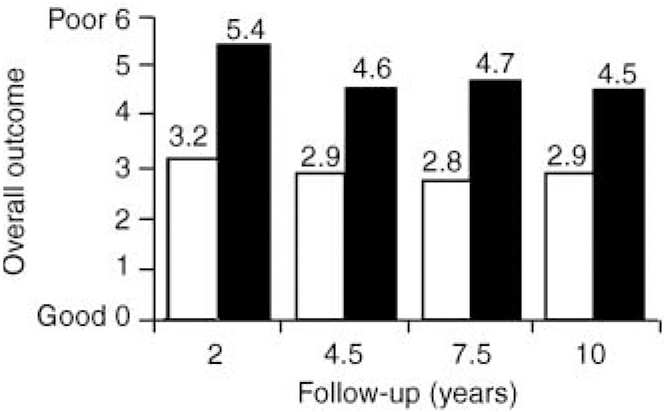
Ten-year outcome: patients with schizoaffective disorders, schizophrenia, affective disorders and mood-incongruent psychotic symptoms | The British Journal of Psychiatry | Cambridge Core
What is a 'mood-congruent' delusion? History and conceptual problems

Psychotic depression - Wikipedia
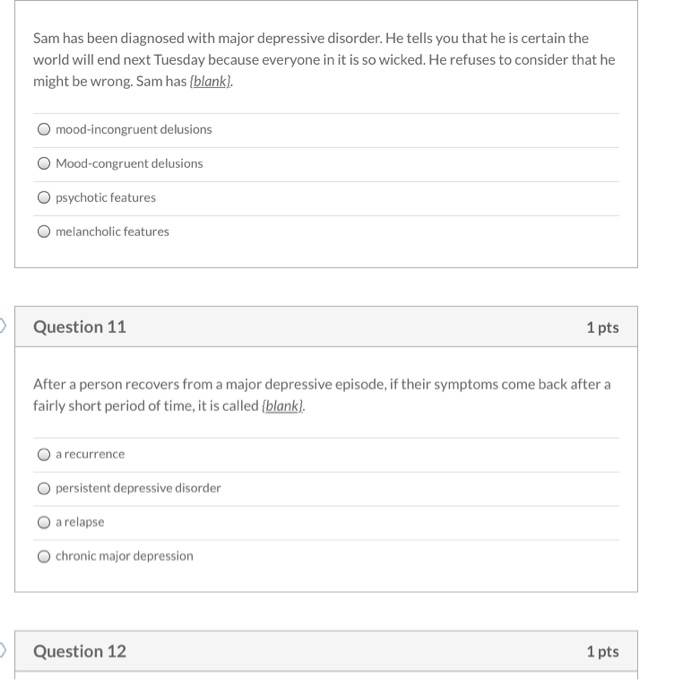
Solved: Sam Has Been Diagnosed With Major Depressive Disor... | Chegg.com

The characteristics of psychotic features in bipolar disorder | Psychological Medicine | Cambridge Core

Psychotic features of the subjects with psychotic major depression (N=24). | Download Scientific Diagram
Schizoaffective disorder and affective disorders with mood-incongruent psychotic features: keep separate or combine? Evidence fr

Schizophrenia, Bipolar Disorder, and the Psychosis Continuum - Psychiatry Advisor
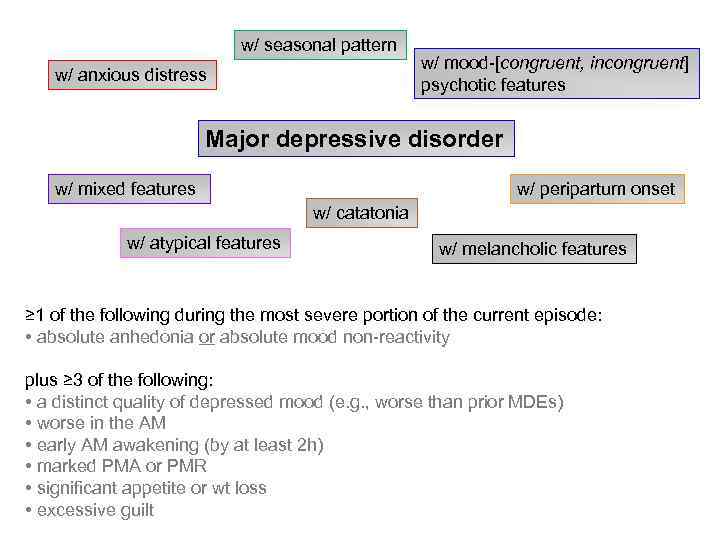
Mood Disorders Prof Anatoly Kreinin MD Ph D
An association study of the neuregulin 1 gene, bipolar affective disorder and psychosis

Exploring the Psychosis-Depression Interface: Clinical Implications
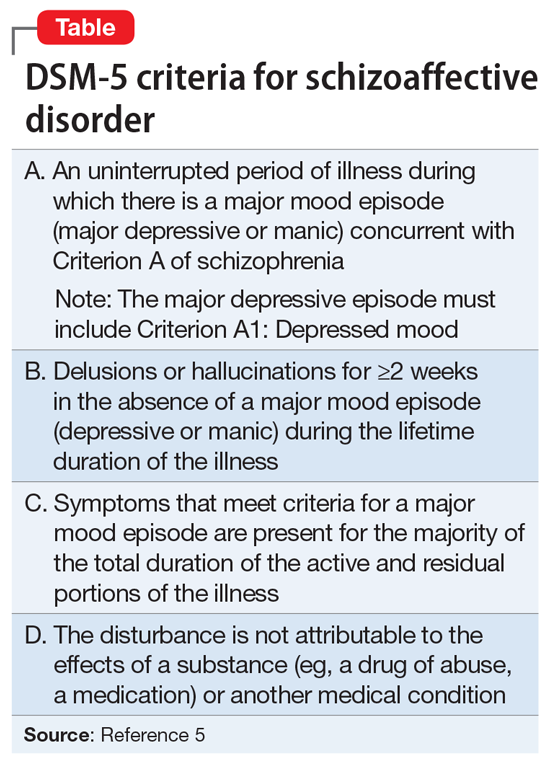
Schizoaffective disorder: A challenging diagnosis | MDedge Psychiatry
Posting Komentar untuk "mood incongruent psychotic features"